What is DHCP?
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a protocol used to assign an IP address, domain name and other configuration information to computers on a network. DHCP is usually enabled on routers and other devices that are connected to the Internet. When a computer connects to the network, it broadcasts a request for an IP address and other configuration information from the DHCP server. The DHCP server then allocates an IP address, domain name and other configuration information to the computer. DHCP is an important protocol for network administrators and users because it allows computers to automatically obtain their IP addresses. However, this feature can also be a security risk. If the DHCP server is not configured properly, it may be possible to obtain unauthorized or incorrect information from the server.
According to Microsoft they define it as a client/server protocol that automatically provides an Internet Protocol (IP) host with its IP address and other related configuration information such as the subnet mask and default gateway.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
a protocol for delivering host-specific configuration parameters from a DHCP server to a host and a mechanism for allocation of network addresses to hosts.
Source: https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc2131Definitions
- DHCP server: The DHCP server is responsible for assigning IP addresses to devices on the network.
- DHCP client: The DHCP client is the device that requests an IP address from the DHCP server.
- Lease time: The lease time is the amount of time that a DHCP lease is valid for.
- Renewal: The renewal process is used to extend a DHCP lease when it expires.
- Rebinding: Rebinding is used to reassign a DHCP lease to a new device.
- Release: The release process is used to terminate a DHCP lease.
- Static IP addresses: Static IP addresses are assigned manually
Purpose of DHCP
- allow hosts to dynamically learn their network configurations such as IP, DNS, Mask, Default gateway, etc
- modern networks used it
- home networks usually the DHCP role is performed by the router it self
- meant for client devices such as laptops, phones, etc. to obtain unique IP addresses
- not meant for servers, printers, routers, firewalls and switches because they need manual configuration such as static IP
- Corporate networks run a DHCP server such Windows Server or a Linux box
Functions of DHCP
Try to understand the DHCP process called DORA to know how DHCP function.
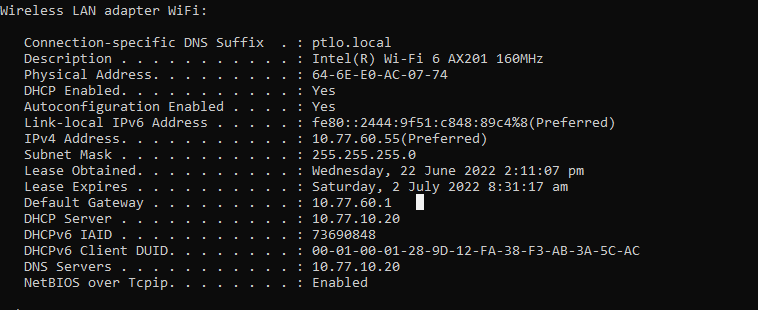
ipconfig /all #Display IP Configurations- Network Adapter configurations
- Obtain an IP address automatically
- Obtain DNS server address automatically
- DHCP servers uses UDP 67
- DHCP clients uses UDP 68
DORA
DORA is the process that is used by DHCP. It helps in providing unique IP addresses to clients or hosts on the network. The process goes through 4 steps below.
- Discover
- Offer
- Request
- Acknowledge
Commands to initiate the DORA process. If we use packet capture tools like wireshark we can see how the process works in detail.
ipconfig /release #Remove DHCP addressipconfig /renew #Request new records from DHCP serverIn summary, here is what going to happen from the above command.
- Are there any DHCP servers on the network? I need an IP address.
- How about this IP address?
- I want to use the IP address you offered me
- Okay, you may use it
| Discover | Client -> Server | Broadcast |
| Offer | Server -> Client | Broadcast or Unicast |
| Request | Client -> Server | Broadcast |
| Ack | Server -> Client | Broadcast or Unicast |
| Release | Client -> Server | Unicast |
DHCP Relay
We configure a DHCP relay when the router is not the DHCP server, and DHCP clients connected to the router’s connected LAN. And there is no DCHP server in the connected LAN either.
- Configure Router to act as DHCP server for its connected LAN
- Router must be configured as DHCP relay agent if DHCP server is centralized
- It will forward the DHCP request to the server as uni-cast
Routers do not forward broadcast messages
This the reason why we configure DHCP relay.
Benefits of DHCP
- Reliable IP address configuration
- Minimizes configuration errors caused by manual configurations
- Avoid IP address conflicts
- Reduced network administration
Please read this document from Microsoft https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/networking/technologies/dhcp/dhcp-topConfiguring DHCP on Cisco IOS
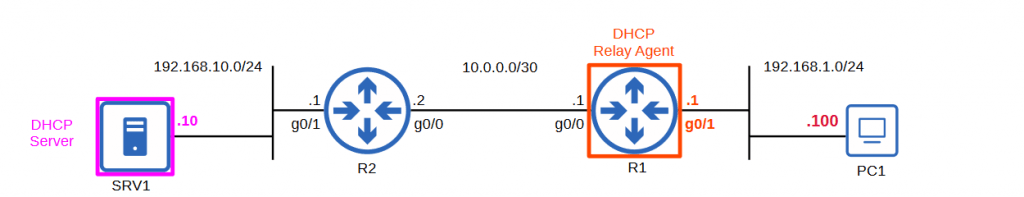
Steps to configure a DHCP server in IOS
- Specify a range of address that won’t be given to DHCP clients
- Create a DHCP pool
- Specify subnet of addresses to be assigned to clients
- Specify DNS server that DHCP clients should use
- Specify the domain name of the network
- Specify the default gateway
- Specify the lease time
Router IOS Commands
Commands used for configuring the router R1.
R1(config)#ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.10R1(config)#ip dhcp pool LAB_POOLR1(dhcp-config)#network 192.168.1.0 /24R1(dhcp-config)#dns-server 8.8.8.8R1(dhcp-config)#domain-name jeremysitlab.comR1(dhcp-config)#default-router 192.168.1.1R1(dhcp-config)#lease 0 5 30DHCP Relay Agent Configuration in IOS
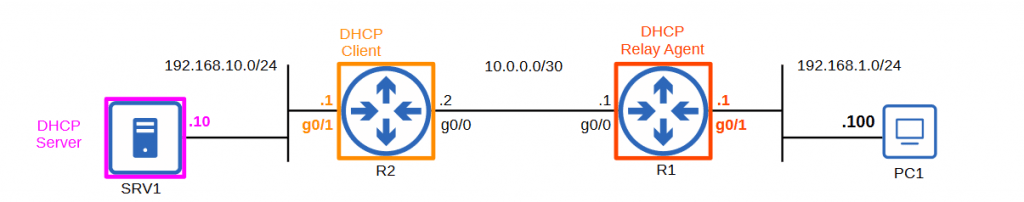
Steps to configure DHCP Relay agent:
- Configure the interface connected to the subnet of the client devices
- Configure the IP address of the DHCP server as the ‘helper’ address
R1(config)#interface g0/1R1(config-if)#ip helper-address 192.168.10.10DHCP Client Configuration in IOS
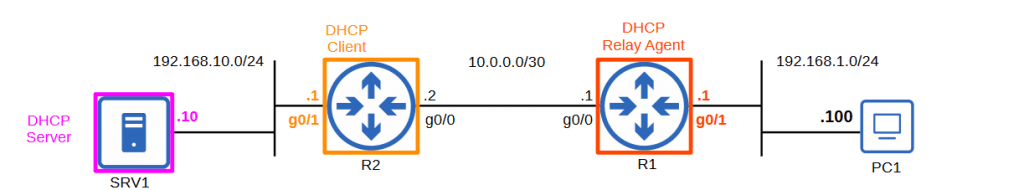
R2(config)#interface g0/1R2(config-if)#ip address dhcp